(1) Complete the following activity to solve the simultaneous equations.
5x + 3y = 9 —–(I)
2x – 3y = 12 —– (II)
Solution
5x + 3y = 9 —–(I)
2x − 3y = 12 —– (II)
Adding equations (I) and (II)
5x + 3y = 9
2x − 3y = 12_
7x = 21
x = `21/7`
x = 3
Putting the value of x = 3 in (I) we get
5x + 3y = 9
5(3) + 3y = 9
15 + 3y = 9
3y = 9 − 15
3y = −6
y = `(-6)/3`
y = −2
Thus, (x, y) = (3, −2)
2 .Solve the following simultaneous equations.
(1) 3a + 5b = 26; a + 5b = 22
Answer:-
3a + 5b = 26 …..(I)
a + 5b = 22 …..(II)
Subtracting (II) from (I)
2a = 4
\[\Rightarrow\] a = 2
Putting the value of a = 2 in (II)
5b = 22 – 2 = 20
\[\Rightarrow\] b = \[\frac{20}{5} = 4\]
Thus, a = 2 and b = 4.
(2) x + 7y = 10; 3x – 2y = 7
Answer:_
x + 7y = 10; …..(I)
3x – 2y = 7 ….(II)
Multiplying (I) with 3
3x + 21y = 30; …..(III)
3x – 2y = 7 ….(IV)
Subtracting (IV) from (III), we get,
23y = 23
y = 1
Putting the value of y in (IV) we get
3x – 2 = 7
⇒ 3x = 7 + 2 = 9
⇒ 3x = 9
⇒ x = 3
Thus, (x, y) = (3, 1)
(3) 2x – 3y = 9; 2x + y = 13
Answer:-
2x – 3y = 9 ….(I)
2x + y = 13 …..(II)
Subtracting (I) from (II) we get
2x – 3y = 9
2x + y = 13
– – –
0 –4y = –4
y = `(-4)/(-4)`
y = 1
Substitute y = 1 in equation (II)
2x + y = 13
2x + 1 = 13
2x = 13 − 1
2x = 12
x = `12/2`
x = 6
Thus, (x, y) = (6, 1)
(4) 5m – 3n = 19; m – 6n = -7
Answer:-
5m – 3n = 19 …..(I)
m – 6n = –7 …..(II)
Multiplying (I) with 2 we get
10m – 6n = 38 …..(III)
Subtracting (II) from (III) we get
\[10m – m – 6n – \left( – 6n \right) = 38 – \left( – 7 \right)\]
\[ \Rightarrow 9m = 45\]
\[ \Rightarrow m = \frac{45}{9} = 5\]
Putting the value of m = 5 in (II) we get
\[5 – 6n = – 7\]
\[ \Rightarrow – 6n = – 7 – 5\]
\[ \Rightarrow – 6n = – 12\]
\[ \Rightarrow n = \frac{- 12}{- 6} = 2\]
Thus, (m, n) = (5, 2).
(5) 5x + 2y = -3; x + 5y = 4
Answer:-
5x + 2y = –3 …..(I)
x + 5y = 4 …..(II)
Multiply (II) with 5 we get
5x + 25y = 20 …..(III)
Subtracting (III) from (I) we get
\[5x – 5x + 2y – 25y = – 3 – 20\]
\[ \Rightarrow – 23y = – 23\]
\[ \Rightarrow y = \frac{- 23}{- 23} = 1\]
Putting the value of y = 1 in (II) we get
\[x + 5\left( 1 \right) = 4\]
\[ \Rightarrow x + 5 = 4\]
\[ \Rightarrow x = 4 – 5 = – 1\]
Thus, (x, y) = (−1, 1)
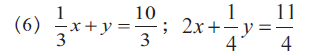
Solve the following simultaneous equation.
\[\frac{1}{3}x + y = \frac{10}{3}; 2x + \frac{1}{4}y = \frac{11}{4}\]
\[\frac{1}{3}x + y = \frac{10}{3} . . . . . \left( I \right)\]
\[2x + \frac{1}{4}y = \frac{11}{4} . . . . . (II)\]
Multiply (I) with 3 and (II) with 4
\[x + 3y = 10 . . . . . \left( III \right)\]
\[8x + y = 11 . . . . . \left( IV \right)\]
Multiply (IV) with 3
24x + 3y = 33 …..(V)
Subtracting (V) from (III)
\[x – 24x + 3y – 3y = 10 – 33\]
\[ \Rightarrow – 23x = – 23\]
\[ \Rightarrow x = 1\]
Putting the value of x = 1 in (III)
\[1 + 3y = 10\]
\[ \Rightarrow 3y = 10 – 1 = 9\]
\[ \Rightarrow y = \frac{9}{3} = 3\]
Thus, (x, y) = (1, 3)
(7) 99x + 101y = 499; 101x + 99y = 501
Answer:-
101x + 99y = 501 …..(II)
Adding (I) and (II)
200x + 200y = 1000
99x + 101y = 499 …..(I)
or, x + y = 5 ……(III)
Subtracting (1) from (2), we get,
2x – 2y = 2
Or, x – y = 1 …..(IV)
Adding (3) and (4), we get,
2x = 6
⇒ x = 3
Putting the value of x in (3), we get,
3 − y = 1
y = 2
∴ y = 2, x = 3.
(8) 49x – 57y = 172; 57x – 49y = 252
Answer:-
49x – 57y = 172 …..(I)
57x – 49y = 252 …..(II)
57x – 49y = 252 …..(II)
Adding equations (I) and (II)
(49x + 57x) + (–57y – 49y) = 172 + 252
106x + (– 106y) = 424
106(x – y) = 424
(x – y) = `424/106`
∴ x – y = 4 …..(III)
Subtracting (II) from (I) we have
(57x – 49x) + [–49y – (–57y)] = 252 – 172
8x + (–49y + 57y) = 80
8x + 8y = 80
8(x + y) = 80
x + y = `80/8`
x + y = 10 …..(IV)
Adding (III) and (IV)
x + x – y + y = 4 + 10
2x = 14
x = 7
Putting the value of x = 7 in (IV) we get
x + y = 10
7 + y = 10
y = 10 – 7
y = 3
Thus, (x, y) = (7, 3).
Practice set 1.2
- Complete the following table to draw graph of the equations –
(I) x + y = 3 (II) x – y = 4
Complete the following table to draw graph of the equations – (I) x + y = 3 (II) x – y = 4
x + y = 3
| x |
3 |
||
| y | 5 | 3 | |
| (x,y) | (3,0) | (0,3) |
x – y = 4
| x |
|
-1 | 0 |
| y | 0 | -4 | |
| (x,y) | (0,-4) |
x + y = 3
| x |
3 |
-2 | 0 |
| y | 0 | 5 | 3 |
| (x,y) | (3,0) | (-2,5) | (0,3) |
x – y = 4
| x |
4 |
-1 | 0 |
| y | 0 | -5 | -4 |
| (x,y) | (4,0) | (-1,-5) | (0,-4) |
