In the given figure, ∠MNP = 90°, seg NQ ⊥seg MP, MQ = 9, QP = 4, find NQ.
Practice Set 2 | Q 2 | Page 38
In the given figure, ∠MNP = 90°, seg NQ ⊥seg MP, MQ = 9, QP = 4, find NQ.
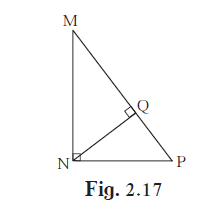
In ∆MNP , <MNP = 90°
NQ perpendicular to MP
MQ = 9 , QP = 4 ,
NQ = ?
We know that,
In a right angled triangle, the perpendicular segment to the hypotenuse from the opposite vertex, is the geometric mean of the segments into which the hypotenuse is divided.
\[\therefore {QN}^2 = MQ \times QP\]
\[ = 9 \times 4\]
\[ = 36\]
\[QN = \sqrt{36}\]
\[ = 6\]
Hence, NQ = 6.
Explanation:-
We are given a right-angled triangle ∆MNP, where <MNP = 90°. We are also given that NQ is perpendicular to MP and MQ = 9 and QP = 4. We need to find the length of NQ.
It is known that in a right-angled triangle, the perpendicular segment to the hypotenuse from the opposite vertex is the geometric mean of the segments into which the hypotenuse is divided. This means that NQ is the geometric mean of MQ and QP.
Therefore, we have:
QN^2 = MQ × QP = 9 × 4 = 36
Taking the square root on both sides, we get:
QN = √36 = 6
Hence, we have found that NQ = 6.
Chapter 2 – Pythagoras Theorem- Text Book Solution
Practice Set 2.1 | Q 2 | Page 38
