Textbook Solution
- Tell the odd one out. Give proper explanation
Q.1: Identify the odd one out in the following:
a) Fuse wire, bad conductor, rubber gloves, generator
Answer: a) Odd one: Bad conductor Explanation: The other items listed (fuse wire, rubber gloves, and generator) all relate to electricity and electric current. A fuse wire stops the flow of electricity if it becomes too strong, rubber gloves protect from electric shocks, and a generator converts mechanical energy into electrical energy. However, a bad conductor does not have a relation to electric current.
b) Voltmeter, Ammeter, galvanometer, thermometer
b) Odd one: Thermometer Explanation: Thermometer measures heat, while the other items listed (voltmeter, ammeter, and galvanometer) measure electric current, potential difference, and small amounts of current respectively in an electrical circuit.
c) Loud speaker, microphone, electric motor, magnet
c) Odd one: Magnet Explanation: The other items listed (loud speaker, microphone, and electric motor) all work on the principles of electrical current, while a magnet has magnetic properties and attracts magnetic substances but has no relation to electrical current.
- Explain the construction and working of the following. Draw a neat diagram and label it.
a. Electric motor
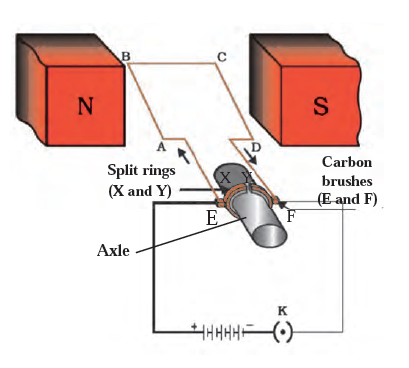
- The electric motor is a device that transforms electrical energy into mechanical energy.
- Principle :-
- Its principle of operation is based on the fact that a current-carrying conductor placed in a magnetic field experiences a force that rotates the conductor and generates mechanical energy.
- Construction:_
- The electric motor consists of an armature coil (ABCD) mounted on an axle, two split rings (P and Q), brushes (X and Y), and a horseshoe electromagnet (NS) with a DC source. The coil is wound around a soft iron core and is positioned between the poles of the electromagnet, allowing it to rotate around its axis.
- working:- In operation, the current enters the coil from the battery through brush X, flows through the coil, and returns to brush Y. Applying Fleming’s left-hand rule, a force is exerted on arm AB that pushes it downward and forces arm CD upward, causing the coil to rotate in a counterclockwise direction.
- After half a rotation, split ring P contacts brush Y and split ring Q contacts brush X, reversing the flow of current and the direction of force acting on the arms of the coil. This causes the coil to continue rotating and complete the next half turn in the same direction, repeating the process and rotating continuously.
b . Electric Generator (AC)
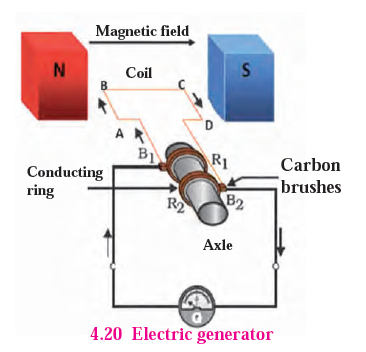
The AC Electric Generator transforms mechanical energy into electrical energy.
Principal :-
It operates based on the principle of electromagnetic induction, where a rotating coil in a magnetic field produces an induced current, the direction of which is determined by Fleming’s right hand rule.
Construction:-
The generator consists of a coil, two slip rings (R1 and R2), brushes (B1 and B2), and a horseshoe-shaped electromagnet. The coil is situated between the poles of the electromagnet, and the brushes are connected to a galvanometer that displays the direction of current in the circuit.
Working:-
As the coil rotates, arm AB moves up and arm CD moves down, causing the coil to rotate in a clockwise direction. The induced current is produced in the direction ABCD. The current flows from brush B2 to B1. After half a rotation, AB is in the place of CD and vice versa, causing the induced current to flow from DCBA. The current then flows from brush B1 to B2. This cycle repeats with every half rotation, reversing the current flow direction, producing an alternating current.
- Electromagnetic induction means
a. Charging of an electric conductor.
b. Production of magnetic field due to a current flowing through a coil.
c. Generation of a current in a coil due to relative motion between the coil and the magnet.
d. Motion of the coil around the axle in an electric motor.
Answer:– C The phenomenon of electromagnetic induction, discovered by Michael Faraday, occurs when there is relative movement between a coil and a magnet, causing a change in magnetic field lines, which in turn induces a current in the coil.
- Explain the difference :
AC generator and DC generator.
Answer:-
AC and DC generators are devices that convert mechanical energy into electrical energy. The main differences between them are:
- Type of Output: A DC generator produces direct current, while an AC generator produces alternating current.
- Method of Generation: In a DC generator, the voltage is generated through commutation, while in an AC generator, the voltage is generated through electromagnetic induction.
- Complexity: AC generators are generally more complex than DC generators, due to the need for the components to handle alternating current.
- Cost: Due to their complexity, AC generators are generally more expensive than DC generators.
- Distribution: Alternating current is more suitable for long distance power transmission, as it can be easily transformed to high or low voltage levels, while direct current requires intermediate conversion steps.
- Efficiency: AC generators tend to be more efficient than DC generators, as they have fewer moving parts.
- Application: DC generators are commonly used for industrial purposes, such as welding, while AC generators are used for producing electricity for homes and commercial buildings.
- Which device is used to produce electricity? Describe with a neat diagram.
a. Electric motor
b. Galvanometer
c. Electric Generator (DC)
d. Voltmeter
Answer:- C Electric Generator (DC)
- How does the short circuit form? What is its effect?
Answer:-
- Contact between live wire and neutral wire causes short-circuiting
- Short-circuiting leads to a large amount of current flow due to low resistance
- Large current flow produces a large amount of heat, leading to potential electrical fires
- Short-circuiting may damage electrical appliances and result in electric shocks
- Hence, short-circuiting is dangerous.
7 Give Scientific reasons.
Que:- Tungsten metal is used to make a solenoid type coil in an electric bulb.
Answer:_
- Tungsten is a strong metal with a high melting point of 3380°C.
- Its strength and high melting point make it ideal for use in light bulbs.
- The bulb produces a large amount of heat and a high temperature when it is in use.
- Tungsten is used because it is able to withstand this intense heat and high temperature without melting or becoming damaged.
B. In the electric equipment producing heat e.g. iron, electric heater, boiler, toaster etc, an alloy such as Nichrome is used, not pure metals.
Answer:_
- Resistivity of alloys such as Nichrome is higher than pure metals, making them more prone to heating when a small amount of current flows through them.
- They have a high melting point and don’t oxidize easily at high temperatures.
- As a result, alloys such as Nichrome are used in electrical equipment that generate heat, like irons, electric heaters, boilers, toasters, etc., instead of pure metals.
C For electric power transmission, copper or aluminum wire is used.
Answer:-
- Copper and aluminum are good conductors of electricity due to their abundance of free electrons.
- Their low resistivity and cost-effectiveness make them a popular choice for electric power transmission.
- Copper and aluminum wires are commonly used for transmitting electricity because of their electrical conductivity and affordability.
D In practice, the unit kWh is used for the measurement of electrical energy, rather than joule.
Answer:_
- The unit of joule is very small for measuring electrical energy.
- The unit kWh is more commonly used for measuring electrical energy as it provides a larger magnitude.
- 1 kWh is equal to 3.6 million joules (3.6 × 106 J).
- Which of the statement given below correctly describes the magnetic field near a long, straight current carrying conductor?
a. The magnetic lines of force are in a plane, perpendicular to the conductor in the form of straight lines.
b. The magnetic lines of force are parallel to the conductor on all the sides of conductor.
c. The magnetic lines of force are perpendicular to the conductor going radially outward.
d. The magnetic lines of force are in concentric circles with the wire as the center, in a plane perpendicular to the conductor.
Answer:_ d
The magnetic lines of force are in concentric circles with the wire as the center, in a plane perpendicular to the conductor.
- The magnetic field lines generated by a current-carrying wire are concentric circles around the wire, with their plane perpendicular to the straight wire.
- To observe the magnetic field, iron filings can be sprinkled on a cardboard with a straight, long wire passing through the center, connected to a battery, key, rheostat, and ammeter.
- When a current passes through the wire, the iron filings will be arranged in the form of concentric circles around it, demonstrating the magnetic field.

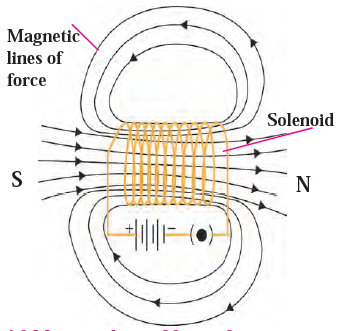
- What is a solenoid? Compare the magnetic field produced by a solenoid with the magnetic field of a bar magnet. Draw neat figures and name various components
Answer:_ A solenoid is a coil of many circular turns of insulated copper wire wrapped closely in the shape of a cylinder.
Similarities:
- Both a solenoid and a bar magnet produce a magnetic field with similar properties.
- The magnetic field lines of both are closed continuous curves.
- Both have magnetic fields that emerge from a North pole and end at a South pole.
- Neither have magnetic field lines that intersect.
- Both attract magnetic materials.
Dissimilarities:
- The magnetic field strength produced by a solenoid can be increased by adjusting the current, which is not possible for a bar magnet.
- The direction of the magnetic field produced by a solenoid can be changed by reversing the current, but this is not possible for a bar magnet.
Q. 10. Name the following diagrams and explain the concept behind them.
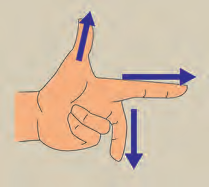

- Fleming’s Right-Hand Rule:
- Used to determine the direction of induced current
- Thumb, forefinger, and central finger are mutually perpendicular
- Forefinger indicates magnetic field direction
- Thumb indicates conductor motion direction
- Central finger indicates induced current direction
- Fleming’s Left-Hand Rule:
- Used to determine the direction of conductor motion
- Thumb, forefinger, and central finger are mutually perpendicular
- Forefinger indicates magnetic field direction
- Central finger indicates current direction
- Thumb indicates conductor motion direction
Q. 11. Identify the figures and explain their use.

Cartridge type fuse:
- Fitted with expensive appliances such as refrigerator, AC, geyser, TV
- Has a current rating (e.g. 1 A, 2 A, 5 A)
- If current flow exceeds rating, the fuse melts and circuit opens
- Protects the appliance from damage during overloading, short-circuiting, or faults.

Miniature Circuit Breaker (MCB):
- Automatically operated switch
- Trips down and breaks circuit if current exceeds limit during short-circuiting or overloading
- Protects electrical appliances from damage and electrical shocks
- Mainly used in low voltage electrical network.
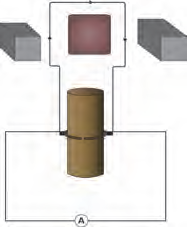
Electric Motor:
- Converts electrical energy into mechanical energy
- Used in electric gadgets such as a fan, juicer, washing machine, mixer, grinder, etc.
12 Solve the following example
a. Heat energy is being produced in a resistance in a circuit at the rate of 100 W. The current of 3 A is flowing in the circuit. What must be the value of the resistance?(Ans : 11 W)
Given:
Power, P =100 W
Current, I = 3 A
Resistance, R = ?
We know, P = I2R
