1. Choose the correct option from the bracket and explain the statement giving reason.(Oxidation,displacement, electrolysis, reduction, zinc, copper, double displacement, decomposition)
a. To prevent rusting, a layer of …….. metal is applied on iron sheets.
Answer:- Answer : a. To prevent rusting, a layer of zinc metal is applied on iron sheets.
b. The conversion of ferrous sulphate to ferric sulphate is …….. reaction.
Answer:-The conversion of ferrous sulphate to ferric sulphate is oxidation reaction.
c. When electric current is passed through acidulated water …….. of water takes place.
Answer:- c. When electric current is passed through acidulated water electrolysis of water takes place.
d. Addition of an aqueous solution of ZnSO4 to an aqueous solution of BaCl2 form a white precipitate is an example of ……. reaction.
Answer:- d. Addition of an aqueous solution of ZnSO4 to an aqueous solution of BaCl2 is an example of double displacement reaction.
Q 2 Write answers to the following.
a. What is the reaction called when oxidation and reduction take place simultaneously? Explain with one example.
he reaction where oxidation and reduction take place simultaneously is called a redox reaction. An example is the reaction between zinc metal and copper(II) ions in aqueous solution to form zinc(II) ions and copper metal.
Zn(s) + Cu2+(aq) -> Zn2+(aq) + Cu(s)
b. How can the rate of the chemical reaction, namely, decomposition of hydrogen peroxide be increased?
Answer:_ he rate of the decomposition of hydrogen peroxide can be increased by:
- Increasing the temperature: Raising the temperature increases the kinetic energy of the reactant particles, leading to more collisions and a higher rate of reaction.
- Adding a catalyst: A catalyst is a substance that increases the rate of a chemical reaction by lowering the activation energy required for the reaction to occur.
- Increasing the concentration of reactants: Increasing the concentration of hydrogen peroxide increases the number of reactant particles in a given volume, leading to more collisions and a higher rate of reaction.
- Increasing the surface area: Increasing the surface area of the reactants increases the number of collisions and the rate of reaction.
- Increasing the pressure: Increasing the pressure increases the number of collisions and the rate of reaction.
c. Explain the term reactant and product giving examples.
- In a chemical reaction, the “Reactants” are the initial substances that undergo change to form new substances known as “Products”.
- For instance, in the reaction between hydrogen and oxygen to form water, the reactants are H2(g) and O2(g) and the product is H2O(l).
- 2H2(g) + O2(g) -> 2H2O(l)
- Another example is the reaction between iron and sulfur to form iron sulfide, where the reactants are Fe(s) and S(s) and the product is FeS(s).
- Fe(s) + S(s) -> FeS(s)
d. Explain the types of reaction with reference to oxygen and hydrogen. Illustrate with examples.
Answer:- Combination Reaction: In this type of reaction, two or more reactants combine to form a single product.
Example: The reaction between hydrogen and oxygen to form water:
2H2(g) + O2(g) -> 2H2O(l)
- Decomposition Reaction: In this type of reaction, a single reactant breaks down into two or more products.
Example: The decomposition of hydrogen peroxide to form water and oxygen:
2H2O2(l) -> 2H2O(l) + O2(g)
- Displacement Reaction: In this type of reaction, a more reactive element replaces a less reactive element in a compound.
Example: The reaction between iron and copper(II) sulfate to form iron sulfate and copper metal:
Fe(s) + CuSO4(aq) -> FeSO4(aq) + Cu(s)
- Combustion Reaction: In this type of reaction, a substance reacts with oxygen to form CO2 and H2O, releasing heat and light.
- Example: The combustion of hydrogen gas:
2H2(g) + O2(g) -> 2H2O(l) + heat and light.
e. Explain the similarity and difference in two events, namely adding NaOH to water and adding CaO to water
Answer :- Reaction between NaOH and water: NaOH + H2O → Na+ + OH-
Reaction between CaO and water : CaO + H2O → Ca(OH)2 + heat
Similarities:
- 1) Both of the equations are exothermic. It means a lot of heat is evolved during the reaction.
- 2) Both reactions from strong basic solutions.
Differences:
- The type of metal oxide is different (NaOH vs CaO).
- The products of the reactions are different (Na+ and OH- vs Ca(OH)2).
- The reaction between CaO and water releases heat, while the reaction between NaOH and water does not.
- Explain the following terms with examples.
- Endothermic reaction:
In endothermic reaction, heat is either absorbed from the surroundings or heat has to supplied from outside.
It means an endothermic reaction needs or takes in heat to continue.
or example: When a solid ammonium chloride (NH4Cl) is dissolved into water, you will observe that the tube becomes colder.
NH4Cl (s) + H2O → NH4Cl (aq) – Heat
In the above reaction, heat is absorbed from surroundings
b. Combination reaction
Answer:-
Combination reaction: When two or more reactants combine in a reaction to form a single product, it is called a combination reaction.
For example: A magnesium strip is heated in the presence of air to form a new product, i.e., magnesium oxide
(MgO) Mg + O2→ MgO
In the above reaction, the combination of Mg and O2 leads to the formation of manganese oxide.
C. Balanced equation
Answer:-
Balanced equation: When the number of atoms of elements in the reactants is equal to the number of atoms of those elements in the products, such a equation is called ‘balanced equation’.
For example: H2 + O2→ 2H2O In the above table, you can see that number of atoms of reactants are equal to the number of atoms of products.
Thus, the reaction is a ‘balanced equation
D. Displacement reaction
Answer:_
Displacement reaction: The reaction in which the ion of a more reactive element displaces the ion of a less reactive metal by forming its own ions.
Such reaction is called displacement reaction. In short, displacement reaction is a reaction in which a more reactive element displaces the less reactive element to form its new compound.
For example: CuSO4 + Zn → ZnSO4 + Cu In the reaction, Zn2+ ions formed from Zn atoms take the place of Cu2+ ions in copper sulphate (zinc is more reactive).
It means that Zn displaces Cu from CuSO4.
4 Give scientific reasons.
a. When the gas formed on heating limestone is passed through freshly prepared lime water, the lime water turns milky.
Answer:_
When CO2 gas is passed through limewater (CaOH)2, the following reaction occurs: ⇒
Ca(OH)2 + CO2 ——–> CaCO3 + H2O
In this reaction, the contact between limewater and the released gas produces an effervescence, causing the limewater to turn milky. This is a chemical test for the presence of carbon dioxide gas.
- The milky appearance of limewater confirms that the effervescence is caused by carbon dioxide.
- The “lime water turning milky” test is a definitive indicator of the presence of carbon dioxide.
b. It takes time for pieces of Shahabad tile to disappear in HCl, but its powder disappears rapidly
Answer:_
The rate of reaction depends upon the size of the particles of the reactants.
Smaller the size of reactant, higher will be its rate of reaction. Greater the size of reactant, lesser will be its rate of reaction.
On addition of dilute HCl in pieces of Shahabad tile, the rate of reaction is very slow.
On the other hand, on addition of dilute HCl in powder form of Shahabad tile, the rate of reaction is fast because:
c.While preparing dilute sulphuric acid from concentrated sulphuric acid in the laboratory, the
concentrated sulphuric acid is added slowly to water with constant stirring.
- Diluting concentrated sulfuric acid with water releases a large amount of heat, making it dangerous and potentially accident-causing.
- To avoid this, start by taking a required amount of water in a beaker.
- Add a small amount of sulfuric acid into the water.
- Stir the mixture continuously to reduce the amount of heat released.
- The result is a controlled release of only a small amount of heat.
d. It is recommended to use air tight container for storing oil for long time.
Answer:-
- Exposure to air causes air oxidation in oil
- Air oxidation can lead to rancidity, causing a foul smell
- Using an airtight container helps to prevent exposure to air
- Storing oil in an airtight container helps preserve its quality and flavor
- Observe the following picture a write down the chemical reaction with explanation
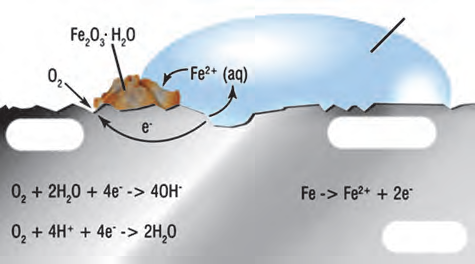
The chemical formula of rust is Fe2O3.H2O.
The rust on iron does not form by a simple reaction of oxygen with iron surface.
The rust is formed by an electrochemical reaction.
Different regions on the surface of iron become anode and cathode.
Fe is oxidised to Fe2+ (anode) Fe (s) → Fe2+ (aq) + 2e-
O2 is reduced to form water (cathode) O2 (g) + 4H+ (aq) + 4 e- → 2H2O
When Fe2+ ions migrate from the anode region they react with water and further get oxidised to form Fe3+ ions.
A redish coloured hydrated oxide is formed from Fe3+ ions.
It is called rust which collects on the surface.
Due to various components of atmosphere, oxidation of metals takes place, consequently resulting in their damage. This is called ‘corrosion’.
Iron rusts and a redish coloured layer is collected on it.
This is corrosion of iron.
- Identify from the following reactions the reactants that undergo oxidation and
reduction.
a. Fe + S ——–> FeS
Answer:-
In the reaction, Fe loses 2 electrons to Sulphur, who accepts them.
This implies that:
- Fe experiences oxidation, resulting in the loss of electrons.
- Sulphur experiences reduction, resulting in the acceptance of electrons.
b. 2Ag2O → 4 Ag + O2
Answer:-
The oxidation state of Ag in Ag2O is +1, while in Ag(s) it is 0.
This indicates that Ag undergoes reduction.
Additionally, the oxidation state of O in Ag2O is -2 and in O2 it is 0.
This signifies that oxygen undergoes oxidation.
c. 2Mg + O2→ 2MgO
First, we write the half reactions:
- Mg0 -> Mg2+ + 2e- (Magnesium goes from 0 to +2, indicating oxidation)
- O2 + 4e- -> O2- (Oxygen goes from 0 to -2, indicating reduction)
In this reaction, Oxygen undergoes reduction, and Magnesium undergoes oxidation.
d. NiO + H2→ Ni + H2O
First write the half reactions:
2H0 – 2e-→ 2H1
Ni2+ + 2e-→ Ni0
⇒ Hydrogen goes from 0 to 1.
Thus, it undergoes oxidation.
⇒ Nickel goes from 2 to 0.
Thus, it undergoes reduction
7 Balance the following equation stepwise.
a. H2S2O7(l) + H2O(l) ———->H2SO4(l)
Balanced equation:
H2S2O7(l) + H2O(l) ———->H2SO4(l)
Explanation:
⇒ Step 1: Write the given unbalance equation H2S2O7 + H2O(l)+ H2SO4(l)
⇒ Step 2: Compare the number of atoms of reactants with the number of atoms of products
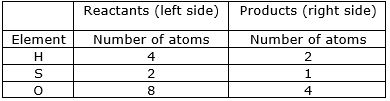
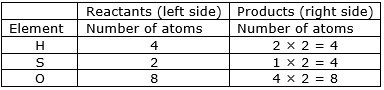
⇒ Step 3: Now, if we multiply 2 in the products, we will get the equal number of atoms as reactants
b) SO2(g) + H2S(aq) → S(s) + H2O (l)
Answer:_
Balanced equation: SO2(g) + 2H2S(aq) 3S(s) + 2H2O (l) Explanation:
⇒ Step 1: Write the given unbalanced equation SO2(g) + H2S(aq) S(s) + H2O (l) ⇒ Step 2: Compare the number of atoms of reactants with the number of atoms of products.
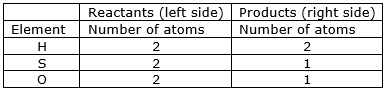
⇒ Step 3: Now, let us consider oxygen atom. If we multiply 2 in the product (in H2O), we will get the equal number of atoms as in reactants (SO2)

⇒ Step 4: Write the resulting equation:
SO2 + H2S S + 2H2O
⇒ Step 5: Now check whether the equation is balanced or not by comparing the atoms
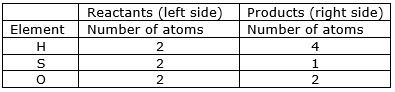
We find that the equation is not balanced yet.
As the number of Sulphur and hydrogen atoms are unequal on the two sides.
First balance the hydrogen number.
⇒ Step 6: Now, let us consider hydrogen atom.
If we multiply 2 in the reactant (in H2S), we will get the equal number of atoms as in product (H2O)
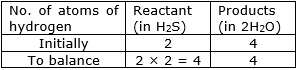
⇒ Step 7: Write the resulting equation: SO2 + 2H2S———> S + 2H2O
⇒ Step 8: Now check whether the equation is balanced or not by comparing the atoms
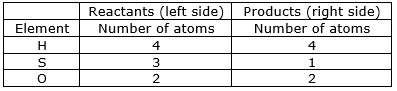
We find that the equation is not balanced yet.
As the number of Sulphur atom is unequal on the two sides.
⇒ Step 9: Now, let us consider sulphur atom.
If we multiply 3 in the product (S), we will get the equal number of atoms as in reactants (SO2 and H2S)

⇒ Step 10: Write the resulting equation: SO2 + 2H2S 3S + 2H2O
⇒ Step 11: Now, compare the atoms of both the sides of all the elements.
Write down the final balanced equation: SO2 + 2H2S 3S + 2H2O
c. Ag(s) + HCl(aq) AgCl + H2
Answer:_ Balanced equation: 2Ag + 2HCl —->2AgCl + H2
Explanation:
⇒ Step 1: Write the given unbalanced equation Ag + HCl AgCl + H2
⇒ Step 2: Compare the number of atoms of reactants with the number of atoms of products.
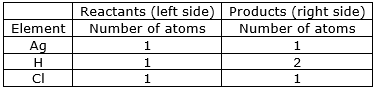
⇒ Step 3: Now, First we consider the element having unequal no. of atoms on both sides.
Thus, let us consider hydrogen atom.
If we multiply 2 in the reactant (in HCl), we will get the equal number of atoms as in product (H2)
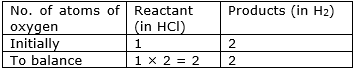
⇒ Step 4: Write the resulting equation:
Ag + 2HCl → AgCl + H2
⇒ Step 5: Now check whether the equation is balanced or not by comparing the atoms
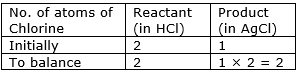
We find that the equation is not balanced yet.
As the number of Chlorine atom is unequal on the two sides.
First balance the chlorine number.
⇒ Step 6: Now, let us consider chlorine atom. I
f we multiply 2 in the product (in AgCl), we will get the equal number of atoms as in reactant (in HCl)
⇒ Step 7: Write the resulting equation:
g + 2HCl 2AgCl + H2
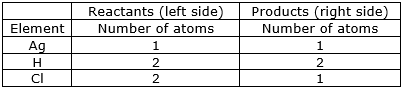
⇒ Step 8: Now check whether the equation is balanced or not by comparing the atoms
We find that the equation is not balanced yet.
As the number of Silver atom is unequal on the two sides.
⇒ Step 9: Now, let us consider silver atom.
If we multiply 2 in the reactant (Ag), we will get the equal number of atoms as in product (AgCl)
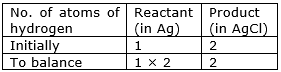
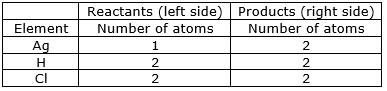
⇒ Step 10: Write the resulting equation:
2Ag + 2HCl 2AgCl + H2
⇒ Step 11: Now, compare the atoms of both the sides of all the elements.
Write down the final balanced equation: 2Ag + 2HCl 2AgCl + H2
D. Balance the following equation stepwise.
NaOH (aq) + H2SO4(aq) → Na2SO4(aq) + H2O(l)
Answer : Balanced equation: 2NaOH + H2SO4Na2SO4 + 2H2O
Explanation:
⇒ Step 1: Write the given unbalanced equation NaOH + H2SO4Na2SO4 + H2O
⇒ Step 2: Compare the number of atoms of reactants with the number of atoms of products.
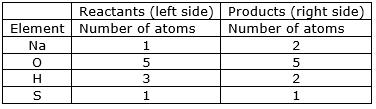
⇒ Step 3: Start by examining the elements with unequal numbers of atoms on both sides. In this case, consider the sodium atom. Multiplying the number of sodium atoms in the reactant, 2NaOH, by 2 results in the same number of sodium atoms as in the product, Na2SO4.
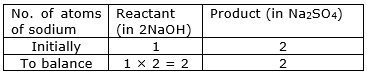
⇒ Step 4: Write the resulting equation:
2NaOH + H2SO4Na2SO4 + H2O
⇒ Step 5: Now check whether the equation is balanced or not by comparing the atoms
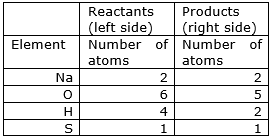
We find that the equation is not balanced yet.
As the number of Oxygen, hydrogen and sulphur atoms are unequal on the two sides.
First balance the hydrogen number.
⇒ Step 6: Now, let us consider hydrogen atom.
If we multiply 2 in the product (in H2O), we will get the equal number of atoms as in reactant (in 2NaOH and H2SO4))

⇒ Step 7: Write the resulting equation:
2NaOH + H2SO4Na2SO4 + 2H2O
⇒ Step 8: Now check whether the equation is balanced or not by comparing the atoms.
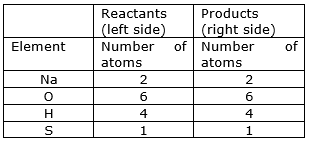
We find that the equation is now balanced yet.
⇒ Step 11: Write down the final balanced equation: 2NaOH + H2SO4Na2SO4 + 2H2O
Que:_ Identify the endothermic and exothermic reaction.
a. HCl + NaOH → NaCl + H2O + heat
Answer:_ Exothermic Reaction
b. 2KClO3(s) 2KCl(s) + 3O2↑
Answer:_ Endo Thermic reaction
c. CaO + H2O → Ca(OH)2 + heat
Answer:_ Exothermic Reaction
d. CaCO3(s) CaO(s) + CO2 ↑
Answer:_ Endothermic reaction
9 Match the column in the following table.
| Reactants | Products | Type of chemical reaction |
|---|---|---|
| BaCl2 (aq) + ZnSO4 (aq) | BaSO4 + ZnCl2 (aq) | Double displacement |
| 2AgCl(s) | 2Ag(s) + Cl2(g) | Decomposition |
| CuSO4 (aq) + Fe (s) | Cu (s) + FeSO4 (aq) | Displacement |
| H2O(l) + CO2(g) | H2CO3(aq) | Combination |
